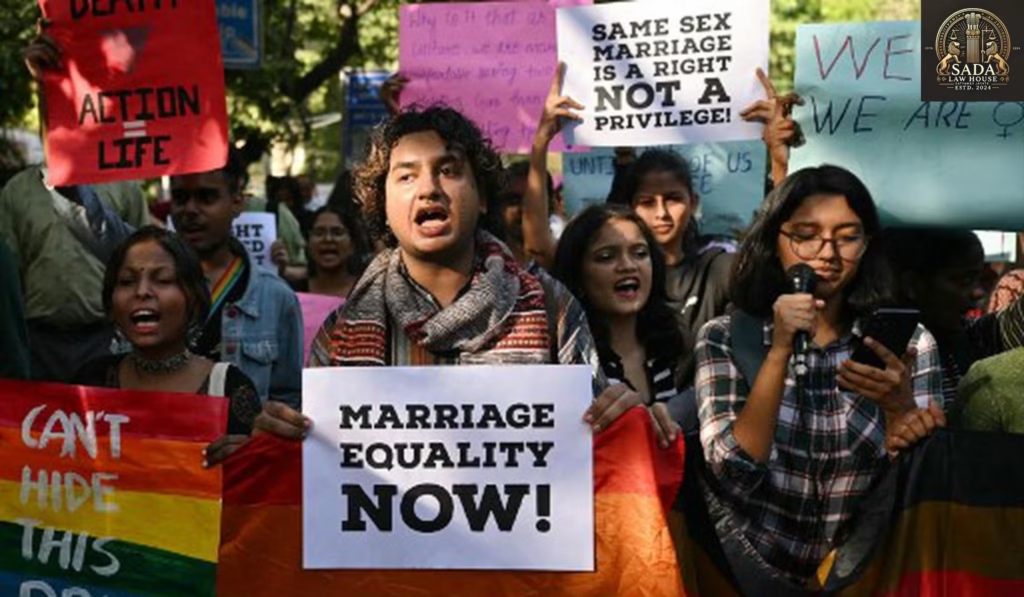Kerala High Court Upholds Transgender Student’s Right to Hostel Accommodation
Trending Today Kerala High Court Upholds Transgender Student’s Right to Hostel Accommodation LEGAL INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITY AT ASTRO ARUN PANDIT LEGAL INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITY AT STRAIVE INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITY AT LEX LAW OFFICES LEGAL INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITY AT PATINE LAW OFFICES LEGAL INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITY AT VANKINA, ALLU & PARTNERS LEGAL JOB OPPORTUNITY AT SNDT WOMEN’S UNIVERSITY, MUMBAI CALL FOR PAPERS BY IILM LAW JOURNAL INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITY AT MINDSPRING ADVISORS, MUMBAI LEGAL JOB OPPORTUNITY AT VAHURA, BANGALORE Kerala High Court Upholds Transgender Student’s Right to Hostel Accommodation KASHISH JAHAN 4 JULY 2025 The Kerala High Court affirms the right of a transgender student to access hostel accommodation according to their gender identity, reinforcing dignity, equality, and inclusion in Indian educational institutions. Introduction: A Landmark Judgment on Gender Equality In a progressive ruling, the Kerala High Court has upheld the rights of a transgender student who was denied hostel accommodation in accordance with her gender identity. The Court ruled that such denial violates the fundamental rights to equality, dignity, and non-discrimination under the Constitution of India. Student’s Struggle for Recognition The petitioner, a postgraduate student, had all legal documents affirming her female gender identity. Despite this, the college denied her a room in the women’s hostel, forcing her to live off-campus, leading to financial hardship and emotional stress. The Court declared this treatment to be in violation of the existing transgender rights framework in India. The NALSA Judgment: A Legal Precedent The judgment heavily cited the landmark case of NALSA v. Union of India, which recognized the right of transgender individuals to self-identify their gender. The Court emphasized that educational institutions must align with this precedent and eliminate arbitrary barriers that infringe on gender identity and basic rights. Court’s Directive to Educational Institutions The High Court ordered the college to immediately allot a hostel room to the student in line with her gender identity. Furthermore, it directed the Government of Kerala to issue comprehensive guidelines to all educational institutions, ensuring that no transgender student faces such discrimination again. The Court also recommended sensitization programs for hostel wardens and administrative staff to create a safer and more inclusive environment. Broader Impact on Campus Inclusion LGBTQ+ rights activists and legal scholars have welcomed this ruling as a milestone for transgender inclusion in higher education. It reinforces that constitutional rights must prevail over institutional biases and logistical excuses. The verdict sets a precedent for universities across the country. Building Inclusive Campuses for All This decision reinforces the idea that educational spaces must reflect the constitutional values of equality, inclusivity, and dignity. By ensuring equal access to hostel accommodation, the judiciary is paving the way for discrimination-free campuses, where every student, regardless of gender identity, can learn and grow without fear or prejudice. Leave a Reply Cancel Reply Logged in as Sadalaw. Edit your profile. Log out? Required fields are marked * Message* Live Cases Kerala High Court Upholds Transgender Student’s Right to Hostel Accommodation Sadalaw • July 4, 2025 • Live cases • No Comments Supreme Court Seeks Centre’s Response on PIL to Regulate Deepfake Content Amid Rising AI Misuse Sada Law • July 1, 2025 • Live cases • No Comments Gujarat High Court Orders Fresh SIT Probe Into Dalit Man’s Custodial Death Amid Allegations of Police Torture Sada Law • July 1, 2025 • Live cases • No Comments 1 2 3 … 5 Next »
Kerala High Court Upholds Transgender Student’s Right to Hostel Accommodation Read More »